By Judy O’Mara, Director, K-State Plant Disease Diagnostic Lab
 Rose rosette is currently showing up in Kansas gardens. This disease is a serious problem in wild multiflora roses but also goes to many common garden roses.
Rose rosette is currently showing up in Kansas gardens. This disease is a serious problem in wild multiflora roses but also goes to many common garden roses.
The rose rosette virus is spread from plant to plant by a microscopic eriophyid mite (Phyllocoptes fructiphilus). It is the only known insect vector of the rose rosette disease. The mite can be wind dispersed or moved around on tools, clothing or infected plant material. Mites can successfully overwinter on the rose plant. The rose rosette virus can also be spread through grafting.
Rose rosette causes a progressive deformity of the rose plant that gets worse over time. It is challenging to identify visually because symptoms vary widely from plant to plant. Some prominent symptoms can include reddish or distorted leaves, stems that are elongated and thickened, a proliferation of shoots (rosette), and excessive thorniness. Plants infected with rose rosette are also more susceptible to winter damage.
An initial symptom of rose rosette might be an elongated stem with reddish  leaves that stands out above the normal growth habit of the shrub. Reddish leaves are a tricky symptom because roses put out new flushes of growth throughout the growing season and the new leaves commonly start out red and then green up.
leaves that stands out above the normal growth habit of the shrub. Reddish leaves are a tricky symptom because roses put out new flushes of growth throughout the growing season and the new leaves commonly start out red and then green up.
More characteristic for rose rosette virus are symptoms of bunchy growth or a proliferation of shoots. This symptom is referred to as a rosette or witches’ broom. Some roses have a bunchy growth pattern so keep in mind that this symptom development should look new or different from the established growth habit of the plant.
A striking symptom for rose rosette is excessive thorniness along the stems. These thorns are generally small, green and soft whereas normal thorns tend to be larger, hard and sharp. Infected plants usually have both types of thorns present.
Pruning out symptomatic portions of infected rose plants will not eliminate the disease.
Plants with rose rosette can survive for one to two years but the virus will continue to spread within a planting. It is important to remove infected plants as soon as possible, including the roots. Infected plants should be placed in trash bags to reduce further spread of the eriophyid mites.
Interspersing roses with non-rose hosts can slow down the spread of the mite and the rose rosette disease. Dead heading roses throughout the growing season will help minimize the habitat of the eriophyid mite. Resistance is not available for commonly grown garden roses. Native roses resistant to rose rosette include: prickly rose (Rosa acicularis ), prairie rose (Rosa arkansana), smooth rose (Rosa blanda), swamp rose (Rosa paulustris), Carolina rose (Rosa carolina), and scotch rose (Rosa spinosissima).
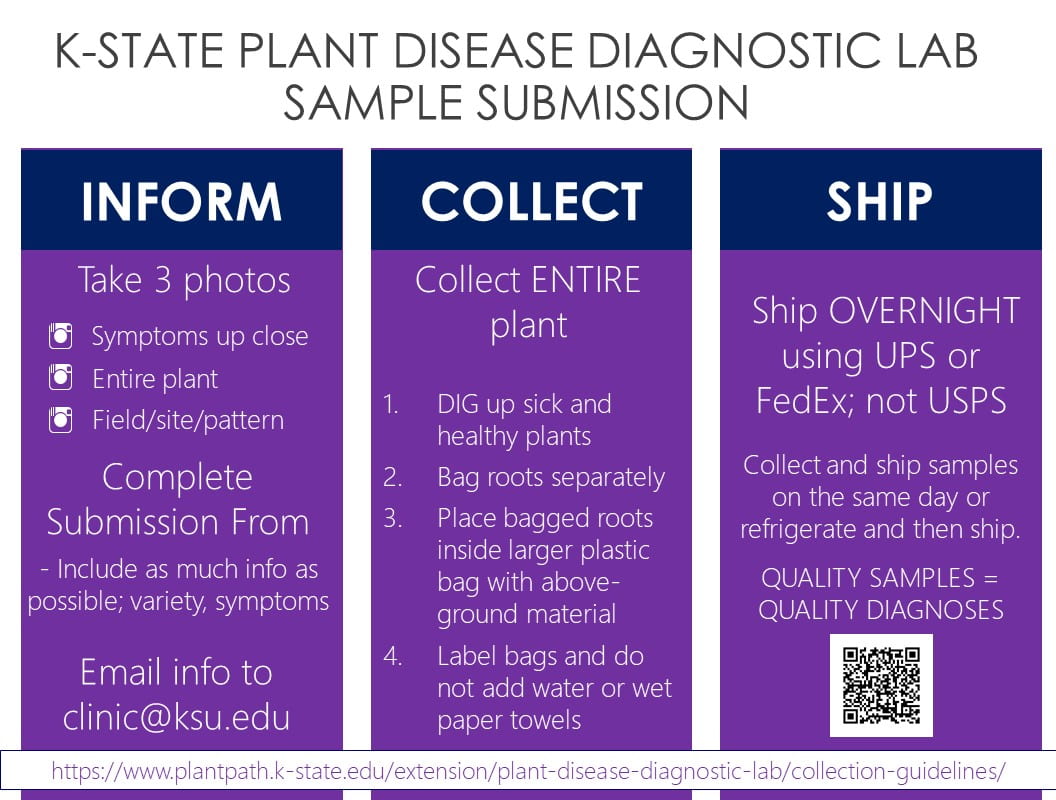
Visual identification of rose rosette virus disease can be challenging. The K-State Plant Disease Diagnostic Lab does offer a PCR test that can confirm the presence of rose rosette virus. Testing can be expensive but might be worthwhile in locations with large plantings of roses.
K-State Plant Disease Diagnostic Lab
4032 Throckmorton PSC
1712 Claflin Road
Manhattan, KS 66506
clinic@ksu.edu
785-532-6176
Useful references:
Rose Rosette Disease: A Diagnostic Guide. N. Claros, etal. https://apsjournals.apsnet.org/doi/10.1094/PHP-05-22-0047-DG
Rose Rosette Disease. J. Olson, etal.
https://extension.okstate.edu/fact-sheets/rose-rosette-disease.html#management-guidelines-for-rrd



 Rose rosette is currently showing up in Kansas gardens. This disease is a serious problem in wild multiflora roses but also goes to many common garden roses.
Rose rosette is currently showing up in Kansas gardens. This disease is a serious problem in wild multiflora roses but also goes to many common garden roses. leaves that stands out above the normal growth habit of the shrub. Reddish leaves are a tricky symptom because roses put out new flushes of growth throughout the growing season and the new leaves commonly start out red and then green up.
leaves that stands out above the normal growth habit of the shrub. Reddish leaves are a tricky symptom because roses put out new flushes of growth throughout the growing season and the new leaves commonly start out red and then green up. Extension personnel across the state have been answering questions about dying/dead trees and shrubs since early spring. Symptoms have ranged from dead, to partially dead, to unusual growth, and late leaf emergence. While it is always good to scout for damaging insects (bagworms anyone?), disease pathogens, and physical injuries such as repeated mower damage to the trunk or recent construction projects that compromised root systems, this year we can blame a lot on our old friend mother nature. Since late summer 2022 through May 2023 rainfall has been scarce, a hard freeze came early, and summer heat exposed any weak landscape plants.
Extension personnel across the state have been answering questions about dying/dead trees and shrubs since early spring. Symptoms have ranged from dead, to partially dead, to unusual growth, and late leaf emergence. While it is always good to scout for damaging insects (bagworms anyone?), disease pathogens, and physical injuries such as repeated mower damage to the trunk or recent construction projects that compromised root systems, this year we can blame a lot on our old friend mother nature. Since late summer 2022 through May 2023 rainfall has been scarce, a hard freeze came early, and summer heat exposed any weak landscape plants. The National Weather Service office in Wichita (@NWSWichita) describes the
The National Weather Service office in Wichita (@NWSWichita) describes the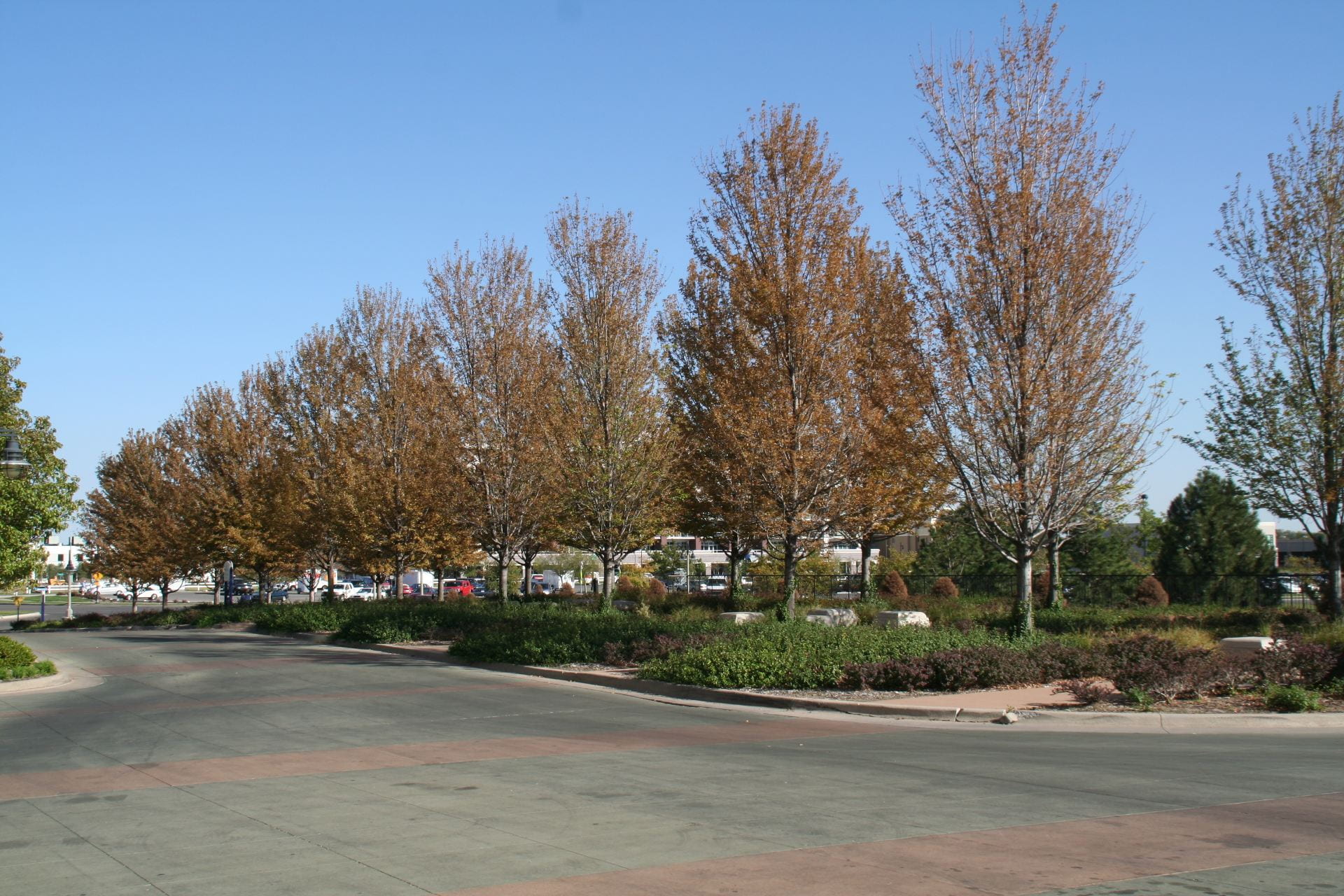




 A brief overview of a few stops that will be seen at the Olathe Horticulture Research Center can be found on the this video. We look forward to seeing you at the Olathe Center on August 3rd!
A brief overview of a few stops that will be seen at the Olathe Horticulture Research Center can be found on the this video. We look forward to seeing you at the Olathe Center on August 3rd!