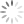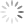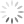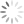Influence of Tall Fescue Baseball Infield Mowing Height on Ground Ball Speed
( By Jared Hoyle, KSU Turfgrass Research and Extension and Gage Knudson, KSU Turfgrass Undergraduate Research Assistant)
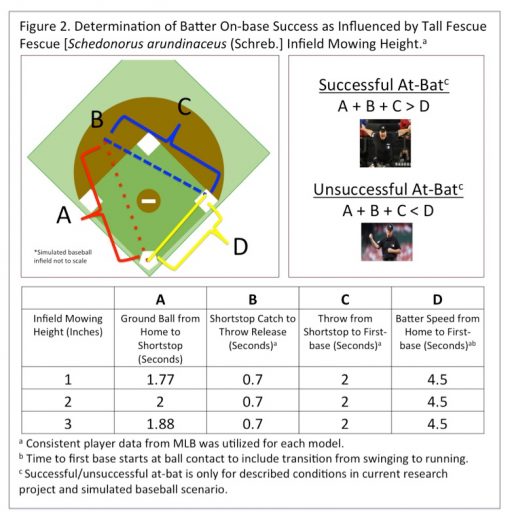
Summary. Athletic field conditions have shown to influence playability. Results of ball-roll speed studies can be used to predict success of infield hits. Field trials were conducted at Rocky Ford Turfgrass Research Center to determine the influence of tall fescue baseball infield mowing height on ground ball speed and batter on-base success. Mowing heights of 2.5, 5, and 7.6 cm resulted in 1.77, 2.08 and 1.88 s ground ball times, respectively.
Rationale. Tall fescue [Schedonorus arundinaceus (Schreb.)] is a drought tolerant turfgrass species commonly used as a baseball infield playing surface. Cultural management practice studies on athletic surfaces have shown direct influences on playability. Minimal information exists on the influence of infield mowing height and ball-roll speed. Results of ball-roll speed studies can be used to predict success of infield hits.
Objectives. Determine the influence of tall fescue baseball infield mowing height on ground ball speed and batter on-base success.
Study Description. Research trials were initiated on November 21, 2016 at the Rocky Ford Research Center (RF) in Manhattan, KS to determine the influence of tall fescue baseball infield mowing height on ground ball speed and batter on-base success. Research trials were conducted on 30.5 m long simulated tall fescue infield. Two experimental runs were conducted on three different infield mowing height treatments; 2.5, 5, and 7.6 cm. Six individual replications of a simulated ground ball were applied to each infield condition and experimental run. Ground balls were applied with a pitching machine set to 112.6 kph. Simulated ground balls were timed in seconds (s) from simulated pitched ball and bat contact (insertion into machine) to baseball fielder location (30.5 m distance). Successful infield hits were calculated using constant athletic ability data and infield ball-roll data. Data was subjected to ANOVA in SAS and means were separated according to Fisher’s protected LSD at 0.05 significance level.
Results. Mowing heights of 2.5, 5, and 7.6 cm resulted in 1.77, 2.08 and 1.88 s ground ball times, respectively (Figure 1). Utilizing ground ball speed results, researchers were able to predict that a simulated batter, if a ground ball was hit to the shortstop position (30.5 m distance), would result in an unsuccessful at bat if a tall fescue infield was mown at 2.5 cm and successful if mown at 5 and 7.6 cm, utilizing consistent player athletic ability data (Figure 1 and Table 1).