(By Jared Hoyle, KSU Turfgrass Research and Extension)
Last Friday, three undergraduate turfgrass science students completed in the Gamma Sigma Delta Undergraduate Research Poster Competition; Dani McFadden, Peyton South and Gage Knudson. Peyton South received 1st place and a 100 dollar monetary prize. Congrats to Peyton and a job well done to Dani and Gage!
Below you can read about the research that they conducted over the past two semesters.
Titles included;
- Effect of Dormant ‘MidIron’ Bermduagrass Colorant Applications on Clothing Blemishing
- Influence of Tall Fescue Baseball Infield Mowing Height on Ground Ball Speed
- The Effect of Human Insect Repellents on Perennial Ryegrass Growth and Recovery

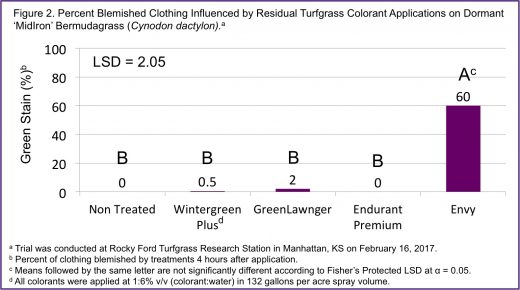
Effect of Dormant ‘MidIron’ Bermduagrass Colorant Applications on Clothing Blemishing
L. McFadden* and J. A. Hoyle*
*Department of Horticulture and Natural Resources, Kansas State University, 2021 Throckmorton Plant Sciences Center, Manhattan, KS; Corresponding author’s email; dmcfadden@ksu.edu
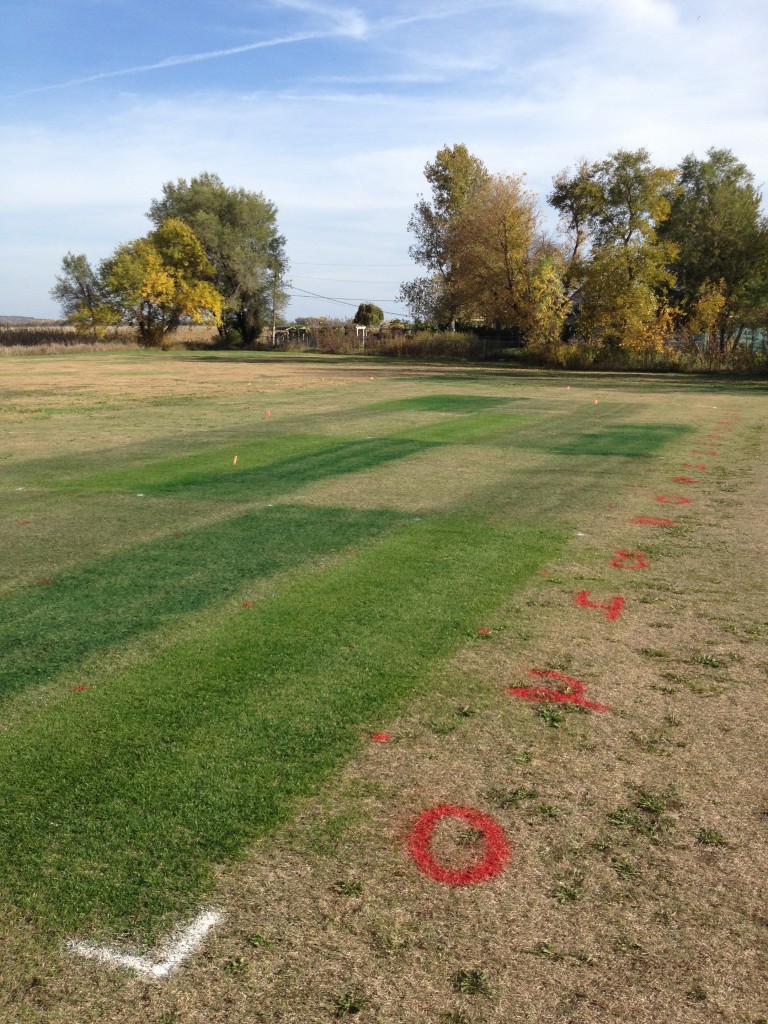
Bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon) is a warm-season turfgrass used on athletic fields in the midwest. Although a desirable turfgrass species for athletic fields it fails to maintain acceptable green color during winter. Turfgrass colorants have been utilized to maintain acceptable green turf color through dormancy periods. Athletes of all ages play on sports fields where colorants have been applied. Extensive research has explored turfgrass colorants on turfgrass quality but minimal research exists on potential clothing blemishing when athletes contact turfgrass applied with colorants. The objective of this research was to determine if turfgrass pigments and paints blemish athletic clothing after the recommended dry time. Researcher’s hypothesis paints would result in greater blemishing and pigments would have no effect due to coloring occurring from inside the plant. Field research trials were initiated Feb. 16, 2017 at Rocky Ford Turfgrass Research Center in Manhattan, KS on dormant ‘MidIron’ bermudagrass maintained at 3.8 cm. Treatments were applied to 1.5 by 1.5 m plots arranged in a randomized complete block design with four replications. Treatments consisted of three paints (Wintergreen Plus, Green Lawnger, Endurant Premium), one pigment (Envy) and a non-treated control for comparison. All colorant treatments were applied at 1:6 (v:v) dilution in 1,234 L ha-1 spray volume. After recommended drying time (4 hrs), a white cotton t-shirt was pulled 1.5 m across the plot weighted down with 11.4 kg. Digital image analysis was used to determine percent blemishing of t-shirt area. Data was subjected to ANOVA in SAS and means were separated according to Fisher’s Protected LSD at 0.05 significance level. Envy (turfgrass pigment) resulted in the highest blemished clothing percentage (60%). All other treatments were no different than the non-treated. Results demonstrate that the tested turfgrass paints safely adhere to the turfgrass canopy and do not blemish athletic clothing.
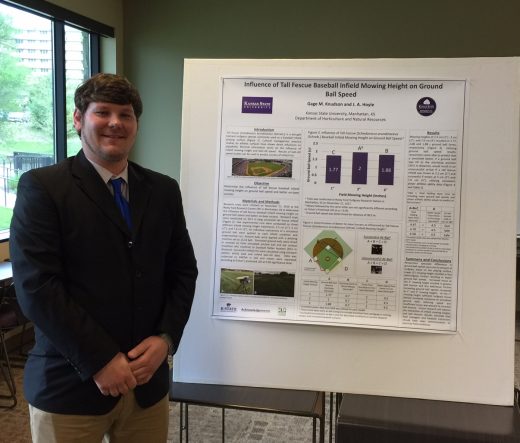
Influence of Tall Fescue Baseball Infield Mowing Height on Ground Ball Speed
Gage M. Knudson* and Jared A. Hoyle*
*Department of Horticulture and Natural Resources, Kansas State University, 2021 Throckmorton Plant Sciences Center, Manhattan, KS; Corresponding author’s email; knudson.gage@gmail.com
Tall fescue [Schedonorus arundinaceus (Schreb.)] is a drought tolerant turfgrass species commonly used as a baseball infield playing surface. Cultural management practice studies on athletic surfaces have shown direct influences on playability. Minimal information exists on the influence of infield mowing height and ball-roll speed. Results of ball-roll speed studies can be used to predict success of infield hits. Research trials were initiated on November 21, 2016 at the Rocky Ford Research Center (RF) in Manhattan, KS to determine the influence of tall fescue baseball infield mowing height on ground ball speed and batter on-base success. Research trials were conducted on 30.5 m long simulated tall fescue infield. Two experimental runs were conducted on three different infield mowing height treatments; 2.5, 5, and 7.6 cm. Six individual replications of a simulated ground ball were applied to each infield condition and experimental run. Ground balls were applied with a pitching machine set to 112.6 kph. Simulated ground balls were timed in seconds (s) from simulated pitched ball and bat contact (insertion into machine) to baseball fielder location (30.5 m distance). Successful infield hits were calculated using constant athletic ability data and infield ball-roll data. Data was subjected to ANOVA in SAS and means were separated according to Fisher’s protected LSD at 0.05 significance level. Mowing heights of 2.5, 5, and 7.6 cm resulted in 1.77, 2.08 and 1.88 s ground ball times, respectively. Utilizing ground ball speed results, researchers were able to predict that a simulated batter, if a ground ball was hit to the shortstop position (30.5 m distance), would result in a unsuccessful at bat if a tall fescue infield was mown at 2.5 cm and successful if mown at 5 and 7.6 cm, utilizing consistent player athletic ability data.

The Effect of Human Insect Repellents on Perennial Ryegrass Growth and Recovery
Peyton E. South* and Jared A. Hoyle*
*Department of Horticulture and Natural Resources, Kansas State University, 2021 Throckmorton Plant Sciences Center, Manhattan, KS; Corresponding author’s email; southpeyton@ksu.edu
Human insect repellents containing diethyltoluamide (DEET) commonly damage turfgrass due to non-target application. Common visual damage results in two areas of healthy growing turfgrass in the shape of footprints with necrotic and chlorotic turfgrass surrounding. Damage results in unacceptable turfgrass quality and playability. Minimal research has been conducted to explore the influence of human insect repellents on turfgrass injury and recovery. Research trials were initiated in November of 2016 at the Throckmorton Plant Sciences Center Greenhouses in Manhattan, KS to determine the influence of human insect repellents on perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) growth and recovery. Perennial ryegrass was established in 10 by 10 cm pots at 387 kg ha-1, maintained at 4.4 cm and were irrigated to prevent drought stress. Greenhouse environment was a 12 hr photoperiod at 15.5°C/ 22.2°C (night/day). Insect repellent treatments were applied to perennial ryegrass plants arranged in a randomized complete block design with 4 replications. Treatments included 9 insect repellents and a non-treated control for comparison. Five treatments contained the active ingredient DEET. Other commonly used insect repellents were also included for comparison. Collected data included visual percent injury on a 0%- 100% scale, where 10% represented maximum acceptable injury. Data was subjected to ANOVA in SAS and means were separated according to Fisher’s protected LSD at 0.05 significance level. All treatments except the control resulted in at least 6% turfgrass injury 1 day after application (DAA). Repel Max (40% DEET) and Off Active (15% DEET) resulted in 68% and 30% injury, respectively 21 DAA. At 21 DAA all other treatments resulted in turfgrass injury similar to the non-treated. Results demonstrate that permanent non-target turfgrass injury will occur if Off Active and Repel Max are applied as a human insect repellent.