(By Jared Hoyle, KSU Turfgrass Research and Extension)
Last week I got a lot of good feed back on the Homeowner Do-It-Yourself Lawn Calendar for Cool-Season Grasses so I decided that it would be good to go ahead and get the warm-season lawn calendar out there for everyone that is manageing zoysiagrass, bermudagrass or buffalograss.
The following is a lawn calendar for zoysiagrass and bermudagrass. Buffalograss, also a warm-season grass, but we will cover that separate because the management of buffalograss is a little different then zoysiagrass and bermudagrass.

Zoysiagrass and Bermduagrass Lawn Calendar
March
Spot treat broadleaf weeds if necessary. Treat on a day that is 50 degrees F or warmer. Rain or irrigation within 24 hours of application will reduce effectiveness.
April
Apply crabgrass preventer between April 1 and April 15, or apply preventer when the eastern redbud is in full bloom. This year we are getting a little warmer sooner but remember this cold snap that we just had would have killed any crabgrass if it had germinated. If using a product with prodiamine (Barricade), apply two weeks earlier. Crabgrass preventers must be watered in before they will start to work.
May – August 15
Fertilize with 1 lb. of nitrogen per 1,000 square feet per application. Follow the recommendations on the bag. More applications will give a deeper green color, but will increase mowing and may lead to thatch buildup with zoysiagrass. Bermudagrass can also have problems with thatch buildup but thatch is less likely with Bermuda than zoysia. Bermudagrass – Use two to four applications. Zoysiagrass – Use one to two applications. Too much nitrogen leads to thatch buildup.
One Application: Apply in June.
Two Applications: Apply May and July.
Three Applications: Apply May, June, and early August.
Four Applications: Apply May, June, July, and early August.
Remember to look and see if you are using a quick release nitrogen source or a slow release nitrogen source. If you use a quick release source then it is immediately available but only lasts a couple weeks. Thats why you would have to make a couple of applications like it is listed above. If you are going to use a slow release source it will tell you on the bag how long the product will last. Therefore, you might not have to make as many applications.
So generally you want to use a total of 2 to 4lb. of nitrogen per 1,000 square feet per year for bermudagrass and 1 to 2 lb. of nitrogen per 1,000 square feet per year for zoysiagrass.
June
If grubs have been a problem in the past, apply a product containing imidacloprid by mid July. Imidacloprid can be applied as early as mid May if there are problems with billbugs or May beetle grubs. These products kill the grubs before they cause damage. They are effective and safe but must be watered in before they become active. June is a good time to core aerate a warm-season lawn. Core aeration will help alleviate compaction, increase the rate of water infiltration, improve soil air exchange and help control thatch.
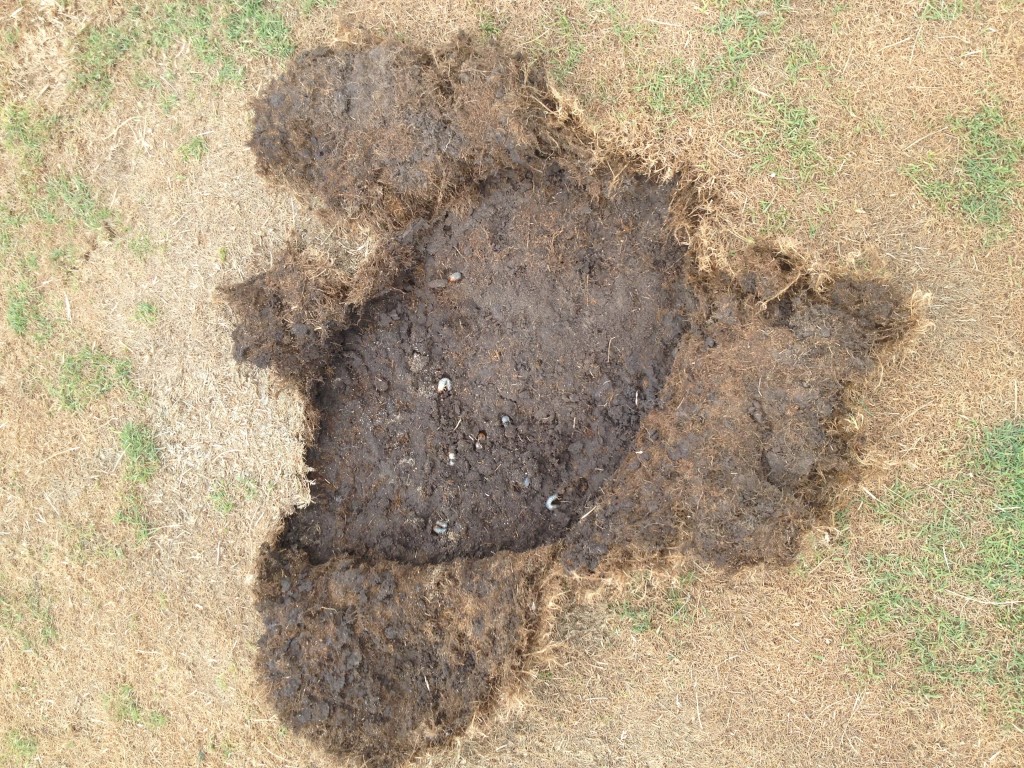

Late-July through August
If you see grub damage, apply a grub killer. If Imidacloprid has been applied, this should not be necessary. Grub killers must be watered in immediately.
Late October
Spray for broadleaf weeds if they are a problem. Treat on a day that is at least 50 degrees F. Rain or irrigation within 24 hours reduces effectiveness. Use the rates listed on the label for all products mentioned.
Buffalograss Lawn Calendar
Buffalograss has become more popular in recent years due to its reputation as a low-maintenance grass. Buffalograss does require less water and fertilizer than our other turfgrasses but often has problems competing with weeds in eastern Kansas. Remember, buffalograss is a low-maintenance lawn and not a “No”-maintenance lawn.
Buffalograss is an open growing grass that will not shade the soil as well as most of our other turfgrasses. Weeds are often the result. A regular mowing schedule can reduce broadleaf weed problems as most broadleaves cannot survive consistent mowing. Those that do either have a rosette growing pattern (dandelions, shepherds purse) or are “creepers” (henbit, chickweed, spurge). Annual grasses such as crabgrass or foxtail can also be a problem. A good weed preventer (prodiamine, pendimethalin or dithiopyr) may be needed prevent problems.

March
Spot treat broadleaf weeds if necessary. The most important treatment for broadleaf weeds should be in late October to early November well after the buffalograss is dormant. Treatments are much more effective then than in the spring as the weeds are smaller and the weeds are sending energy, as well as the herbicide, to the roots. Treatments in March are to take care of any “escapes” missed in the fall spraying. Spray early enough in March that the buffalograss is still dormant. Look at the base of the plants to make sure there is no green. Treat on a day that is 50 degrees F or warmer. Rain or irrigation within 24 hours of application will reduce effectiveness. Use a combination product such as Trimec, Weed-B-Gon or Weed-Out. Weed Free Zone is also good and will give quicker results under cool conditions.
April
Apply crabgrass preventer between April 1 and April 15, or apply preventer when the eastern redbud is in full bloom. If using a product with prodiamine (Barricade), apply two weeks earlier. Crabgrass preventers must be watered in before they will work. Avoid using broadleaf herbicides as the buffalograss is greening up as injury can result. The buffalograss will not be killed but growth will slow making the buffalograss less competitive with weeds.
June
Fertilize with 1 lb. of nitrogen per 1,000 square feet during June. More applications will give a deeper green color, but can encourage weeds. If it is felt that a second application is needed, apply in July.
If grubs have been a problem in the past, apply a product containing imidacloprid by mid July. Imidacloprid can be applied as early as mid May if there are problems with billbugs or May beetle grubs. These products kill the grubs before they cause damage. They are effective and safe but must be watered in before they become active. Again, I would only treat if grubs have been a problem in the past. Note that the whole area may not need to be treated. The beetles that lay the eggs for the grubs are attracted to lights and moist soil and those areas are most likely to be infested.
Late-July through August
If you see grub damage, apply a grub killer. If imidacloprid has been applied or if grubs have not been a problem in the past, this should not be necessary. Grub killers must be watered in immediately.
Late October to Early November
Spray for broadleaf weeds if they are a problem. Look carefully as our winter annuals such as chickweed and henbit are small and easily overlooked. Use a product that contains 2,4-D as it increases effectiveness on dandelions. Treat on a day that is at least 50 degrees F. Rain or irrigation within 24 hours reduces effectiveness. Use the rates listed on the label for all products mentioned.
It is as simple as that! Enjoy!
Always remember to READ THE LABEL for the correct rate, turfgrass tolerance, and specific instructions before application!!!
***Mention of trade names or commercial products in this article is solely for identification purposes and does not imply recommendation or endorsement, nor is criticism implied of similar products not mentioned by Kansas State University.***
Don’t forget to follow me on twitter @KSUTurf.
Also, visit our facebook page www.facebook.com/KSUTurf