–by Cassandra Olds — Livestock and Veterinary Entomology
Biting flies (horn, stable, horse and deer flies) are a common problem encountered by horses. Animals under attack can exhibit a number of fly worry behaviors including skin twitching, leg stamping, tail swishing and general agitation. Horses trying to escape from flies can stampede and injure themselves so effective fly control is essential! Although pyrethroid based sprays can kill flies on horses, a study carried out this summer determined that their repellant effects wore off within 4 hours. In contrast, physical barrier protection through a full body fly sheet, fly boots and fly mask, reduced fly worry behavior by 80-90% and was sustained throughout the day. Physical barriers inhibit the ability of the fly to reach the host skin and take a blood meal, not only does this reduce fly worry but also reduces the risk of pathogen transmission.
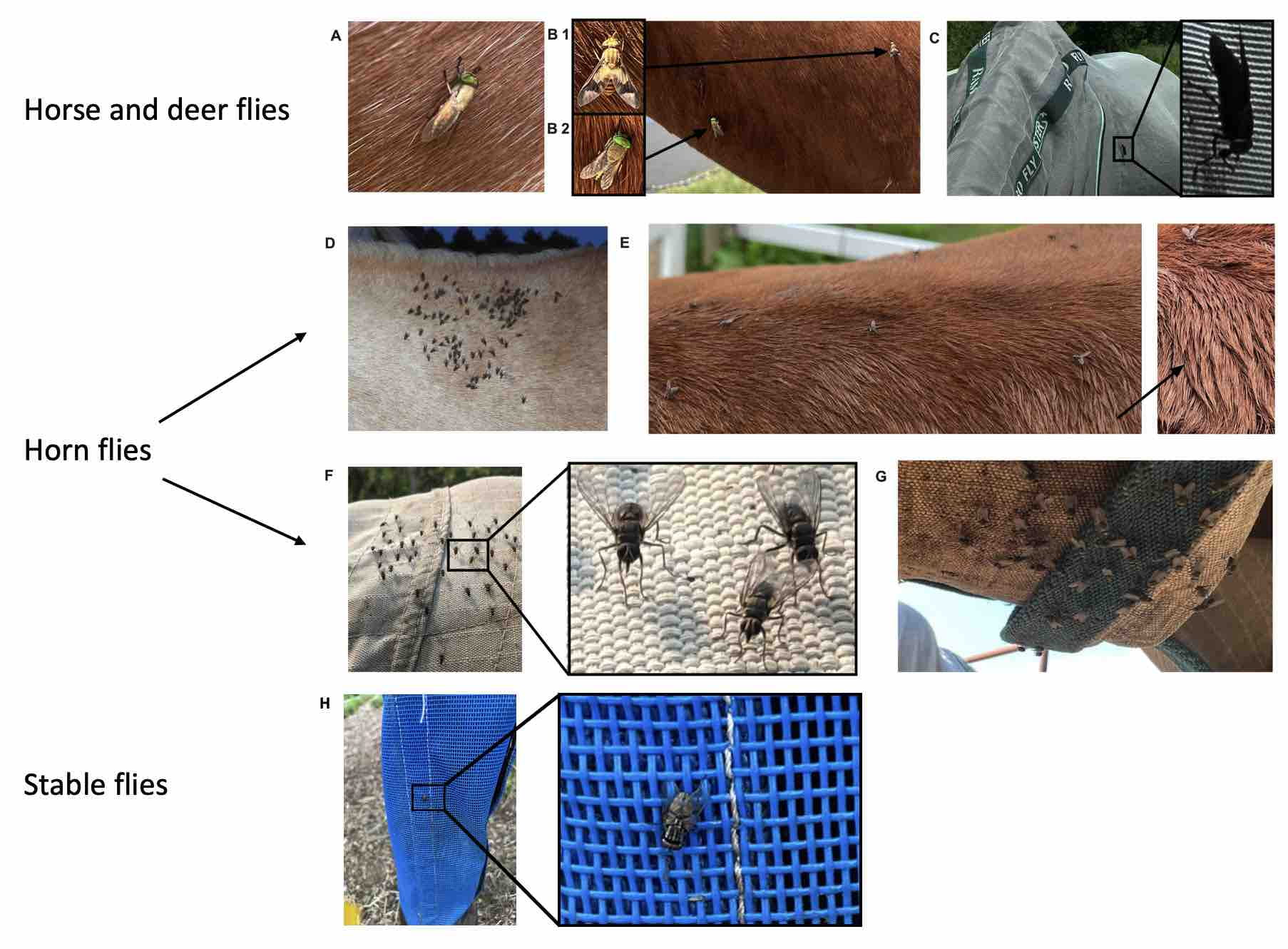
Horse flies (Figure 1 A and B2) and deer flies (Figure 1 B1) both have brightly colored eyes although, the larger black horse fly (Tabanus atratus) (Figure 1 C) can also often be seen. The fly in Figure 1 C was observed trying to feed off a fully covered horse but was unsuccessful and moved onto an uncovered horse nearby where it fed successfully despite attempts from the horse to remove it! Horn flies (Figure 1 D-G) are commonly found on cattle although horses can also be a suitable host. These flies feed 20-30 times a day causing significant fly worry. Horses can often be observed with saliva patches on their back around horn flies (Figure 1 E) indicating repeated attempts to get rid of flies. Horn flies tend to feed together as a group on the neck, withers and belly. Scarring can commonly be seen under the belly in horses with large numbers of flies sustained over a long period. Fly sheets with belly coverings are most effective against horn flies. Stable flies (Figure 1 H) have a strong preference for horse legs, especially front legs. Covering legs though the use of fly boots reduces stamping which can cause stress on the leg and hoof. Best fly protection can be achieved by selecting a well fitted sheet that covers as much of the body as possible (Figure 2). Fly boots come in a variety of types and it is best to select on which can cover as much of the lower leg as possible. Face masks are especially useful in later summer when flies attempt to feed around the horse eye, nose and mouth which can cause irritation and sores. As with all horse gear, check daily for correct fit or signs of rubbing or discomfort!
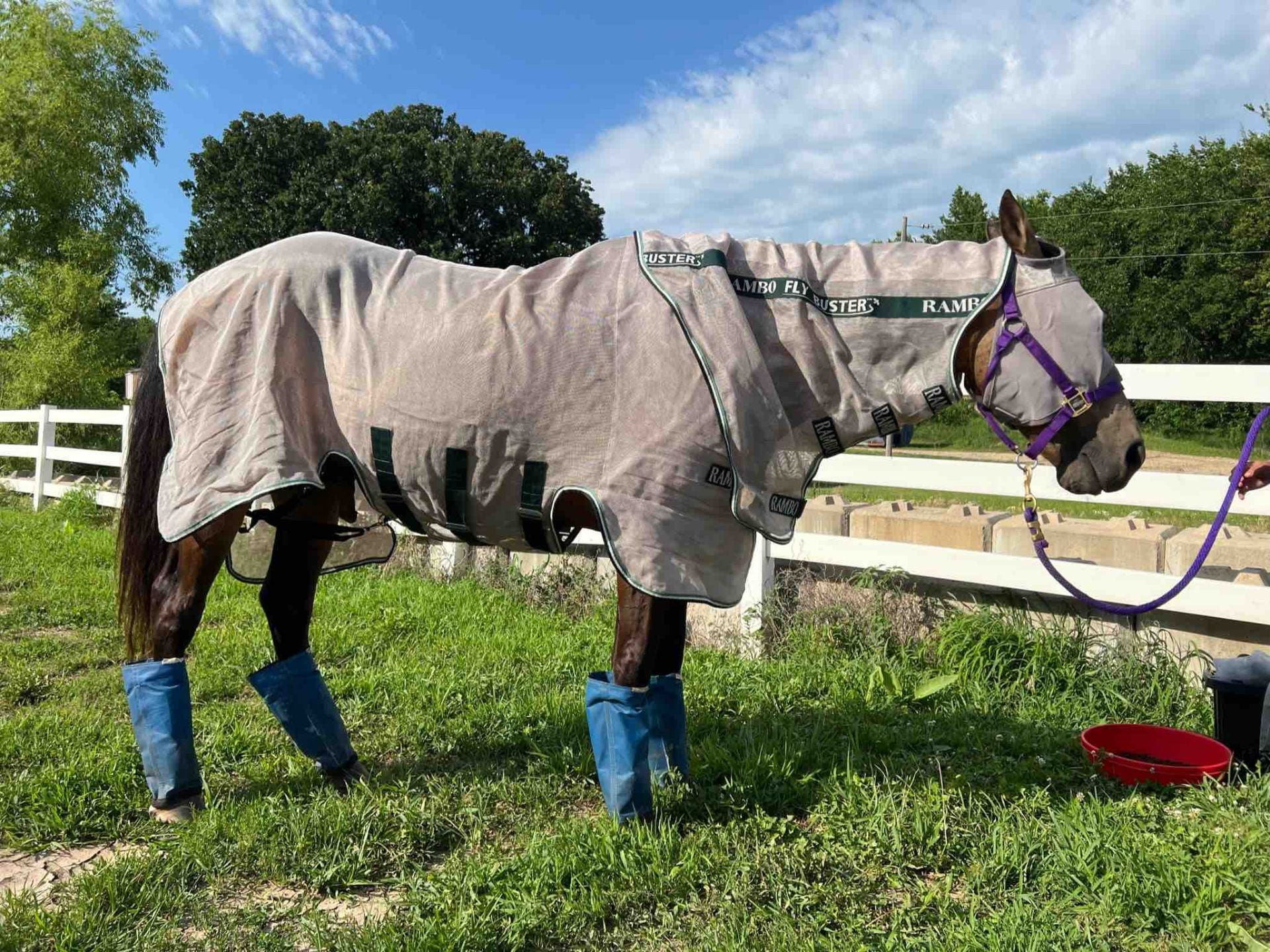

Figure 2: Example of a well fitted full body fly protection