By — Dr. Jeff Whitworth, Dr. Holly Schwarting
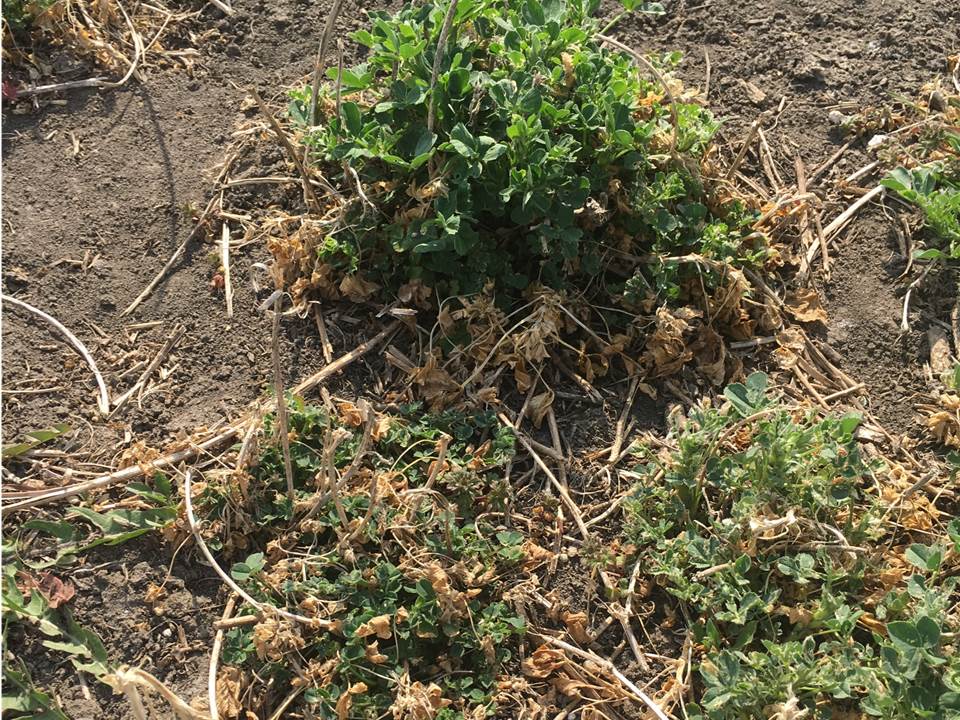
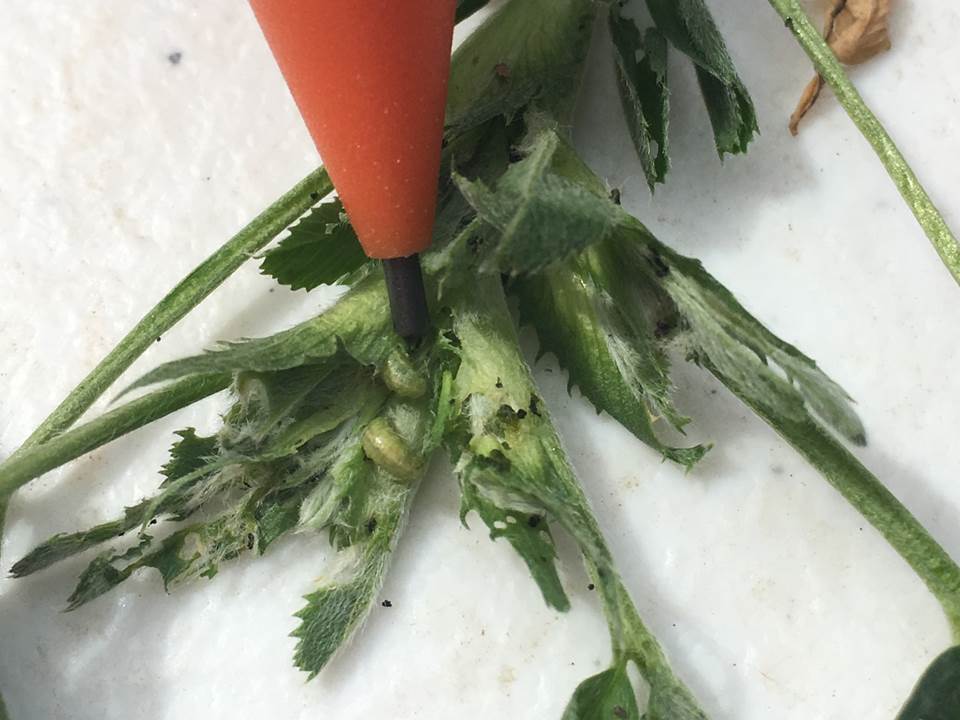
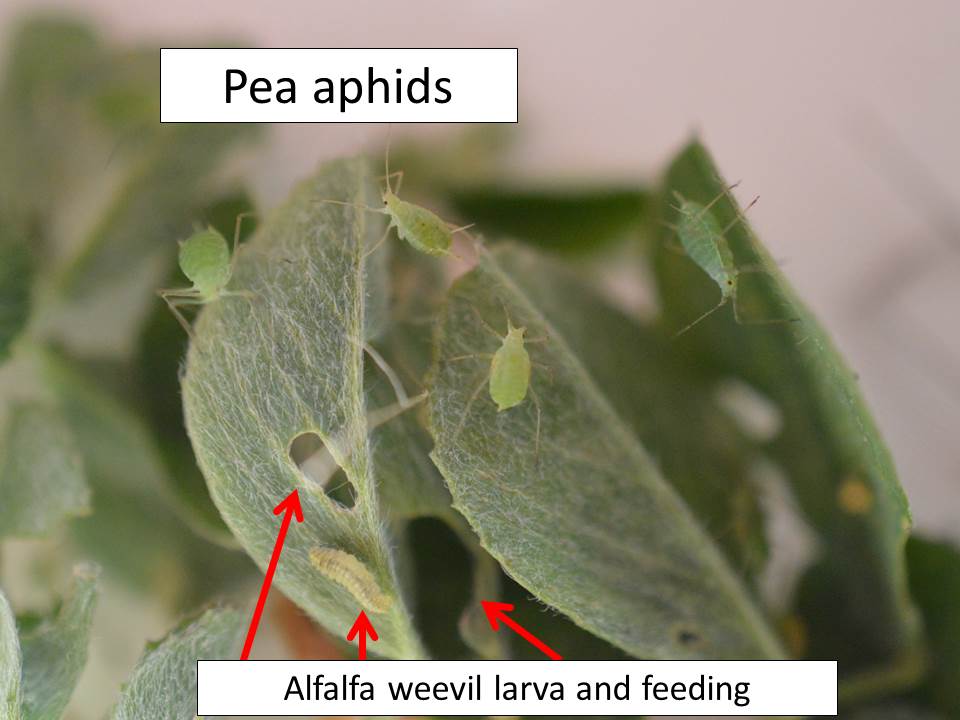
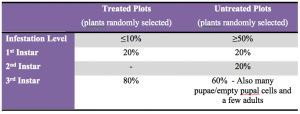
Alfalfa continues to be problematic in NC Kansas. There seems to be many fields of good alfalfa, apparently treated in an effective manner from both an insecticide and a timing standpoint, and not affected by the freezing temperatures earlier this spring. Many of these fields have been, or are being, swathed. However, there are some fields that have had, or are having, a difficult time overcoming the combination of alfalfa weevil larval feeding, early season dry conditions, and the early spring freezing temperatures. In all fields, the early season warmth sped up alfalfa weevil development and feeding, then the cooler temperatures slowed it back down. Alfalfa weevil larvae were 1st detected in NC Kansas in early March. Small, 1st instar larvae are still being detected in some fields.

Some larvae pupated and developed into adults as long as three weeks ago, and they are still in the alfalfa fields. So, NC Kansas still has a significant number of adults. Treating for adult alfalfa weevils is rarely effective, but swathing within 7-10 days should help manage both larvae and adults without an insecticide application.

Adult potato leafhoppers have also been noted in alfalfa fields. These usually migrate into Kansas between the 2nd and 3rd cuttings, so they are about a month early this year.