–by Dr. Jeff Whitworth and Dr. Holly Schwarting
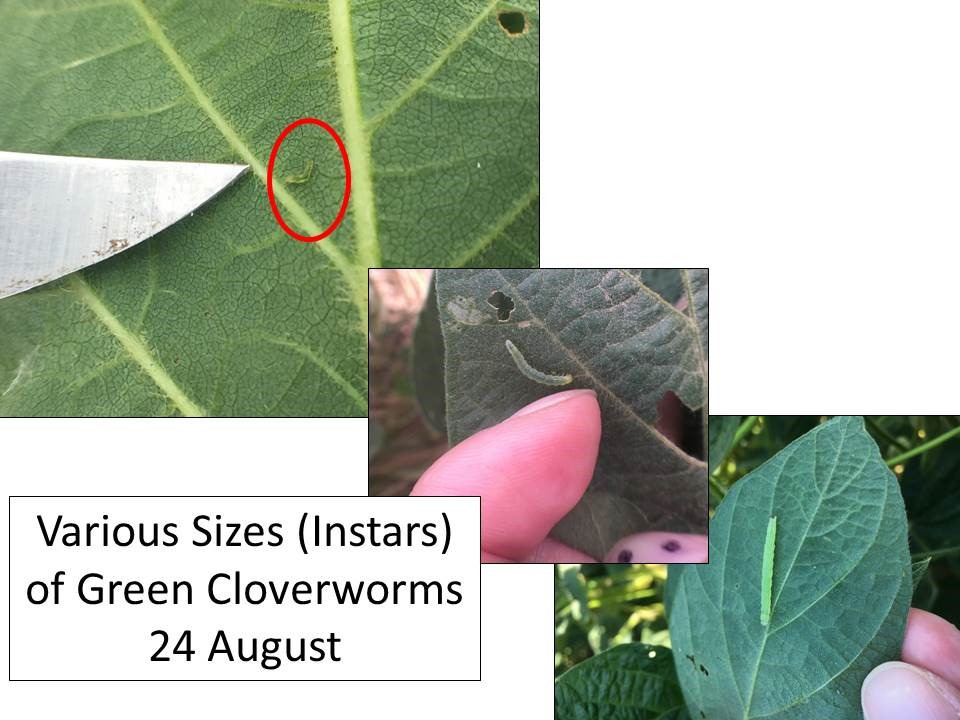
Insect activity is still increasing around north central Kansas. One positive, bean leaf beetles seem to be at really low densities in most fields, at least so far. Green cloverworm larvae are at various developmental stages but there are still many early instars. This means there probably is considerable defoliation to come because, as the larvae get larger, they simply eat more leaf tissue. However, as green cloverworm populations increase, they are often infected with an entomophagous fungus which decimates their populations.
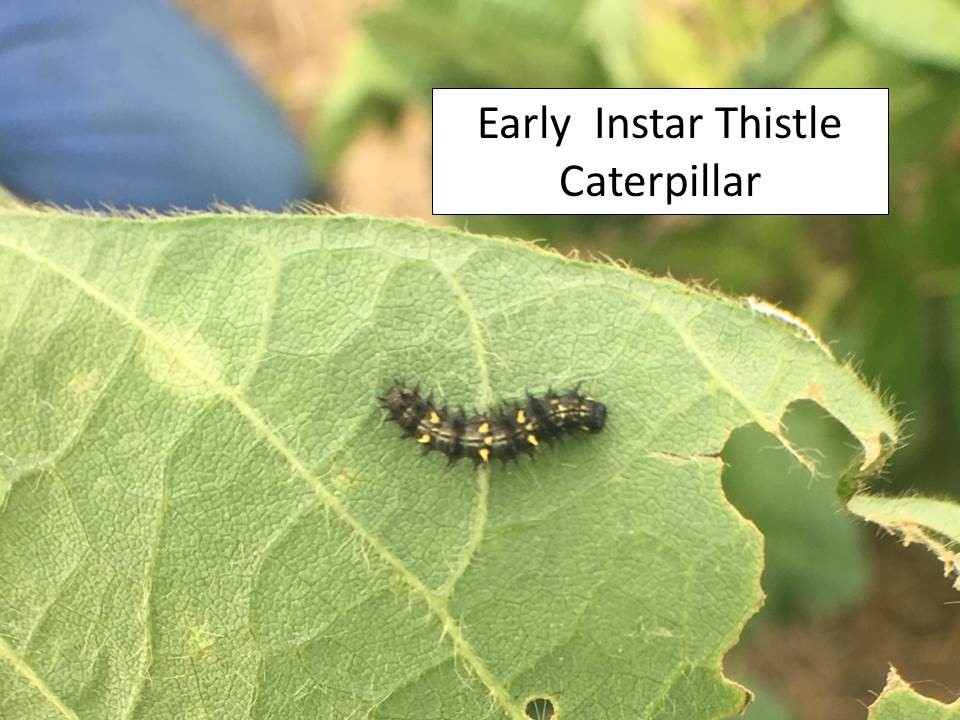
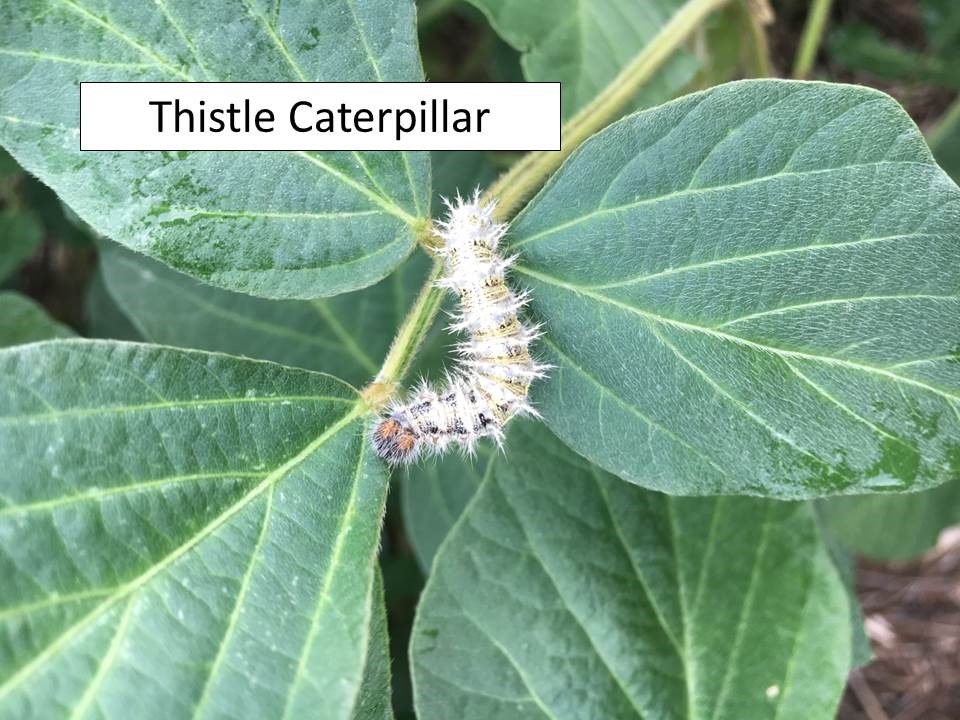
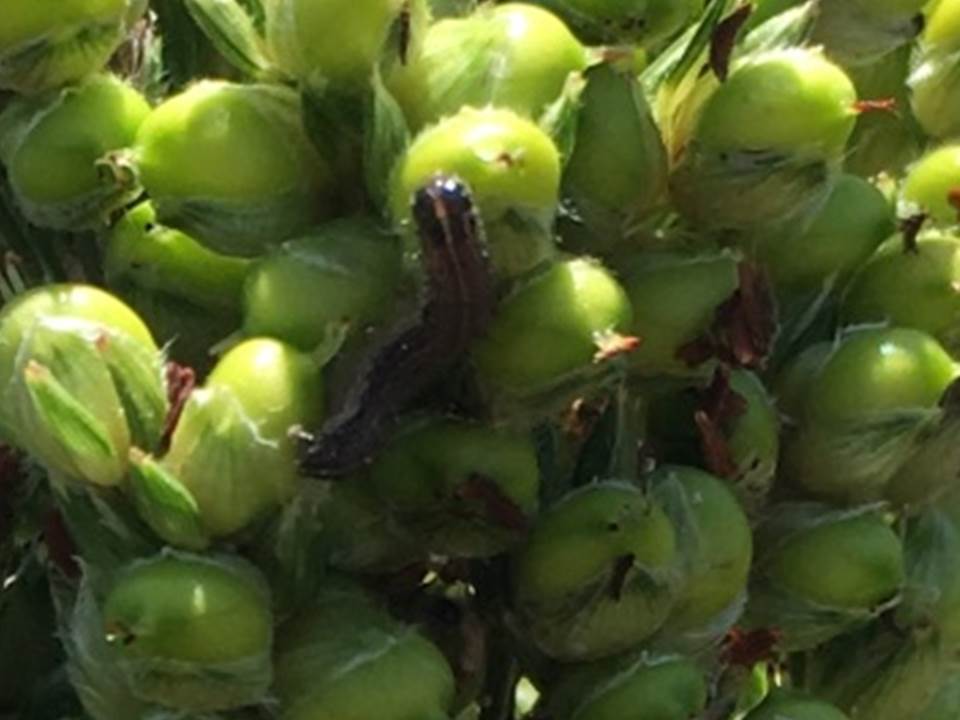
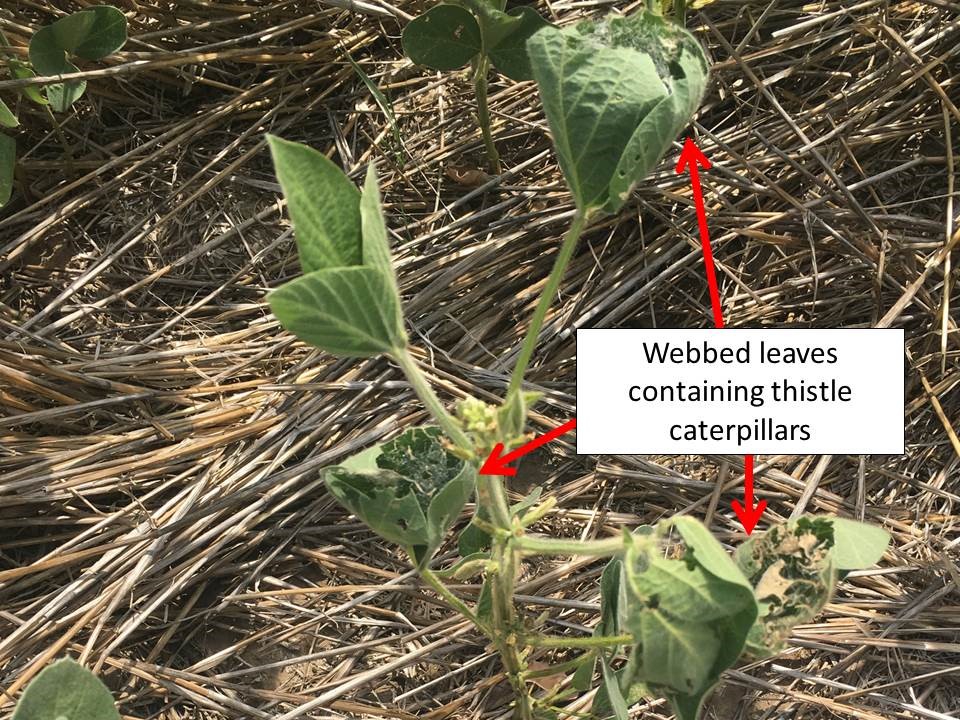
There also are many areas with significant infestations of thistle caterpillars and garden webworms. Both species web leaf tissue around and over themselves, creating a relatively secure area from which they feed on leaves. Many thistle caterpillars are really small right now and may not be noticed yet. So, continued monitoring is important, especially with soybeans just entering the reproductive stages of development.
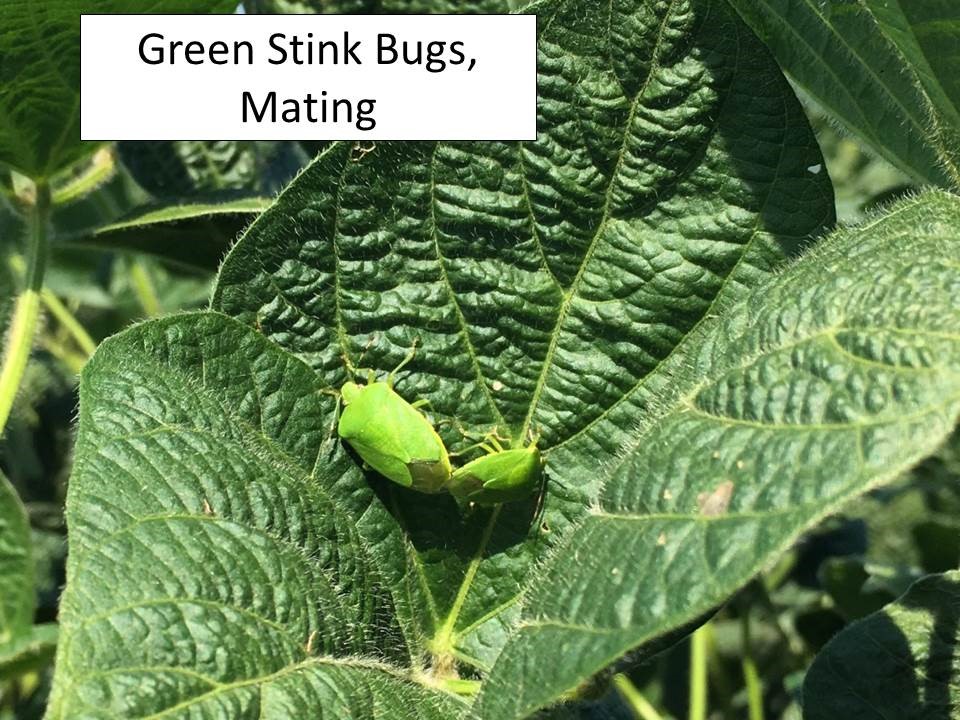
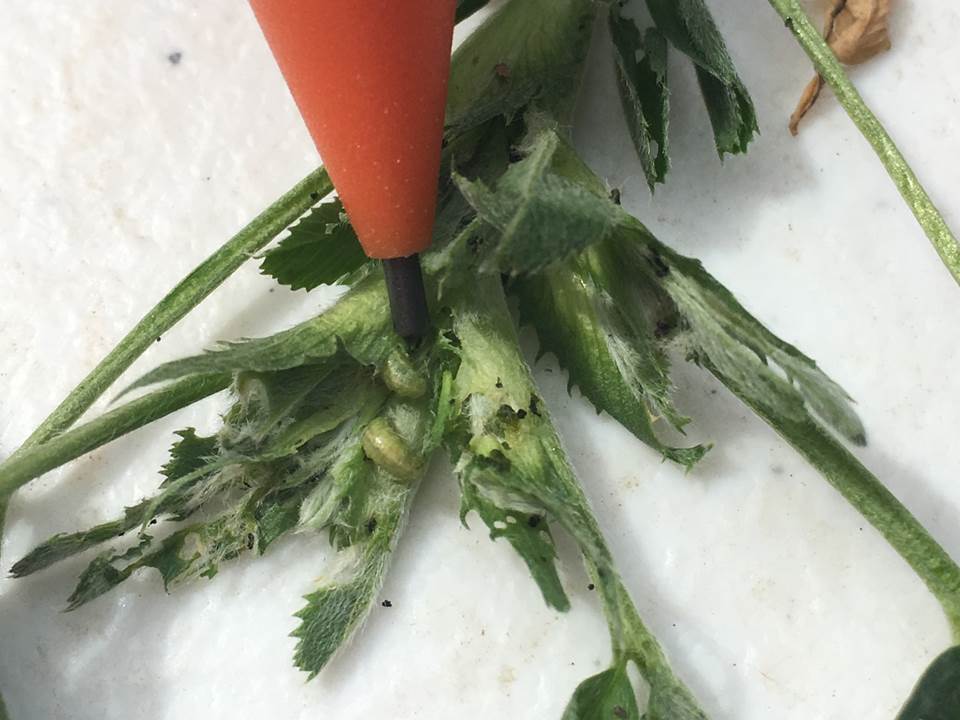
Green stink bugs are relatively common in both conventionally planted and double-cropped soybeans. There are eggs, nymphs, adults, and mating adults all present at this time so sampling needs to be conducted periodically as these bugs can feed on the beans while they are developing inside the pods.
Soybean aphids were detected in double-cropped soybeans in Dickinson Co. on 24 August. Many soybean fields have significant populations of green lacewings and lady beetles, both of which may help control soybean aphids if and when they migrate into these fields. So, as always, please take these into consideration if insecticide applications are contemplated.